What is SEO?
Search engine optimization or SEO is the process of making incremental changes to a website’s code and content so that it will be shown as prominently as possible on search engines and gain as much organic web traffic as possible. SEO can be a complicated process that involves understanding both what your users want and what the search engines want, but it is a highly rewarding exposure strategy that won’t cost you anything in advertising!
This alphabetized list will help you to understand the most important SEO terms, so that you are well equipped to start optimizing your website and climbing those search rankings.

Top SEO terms for beginners
1. Algorithm
Algorithms are digital programs used by apps and search engines to control the way information is retrieved, organized, and displayed to users. In the context of search engines and SEO, numerous algorithms are used to rank the most relevant websites for each search, based on a wide range of ranking factors. In fact, the entire purpose of SEO is to try and make your website appeal to the search engines’ algorithms so that it will show up as prominently as possible in the search engine results.
Algorithms are susceptible to change, and so SEO is a constant process in order to keep up to date with the consistently modified requirements.
2. Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable text that is highlighted when there is a link to another page present within a site’s written content. Web visitors can click on this text to travel to the linked page.
For example, if we were to encourage you to read our Ultimate SEO Checklist (which you definitely should!), the words “Ultimate SEO Checklist” are the anchor text directing you to the article.
For SEO purposes, it’s important to do anchor text correctly. The linked words should always give contextual information for the sake of both your users and search engines as well. Use the appropriate keywords in your anchor text to make it clear what the web page you’re linking to is about. The more descriptive your anchor text, the more authority search engines will attribute to the link, and to your website as a whole.
Using phrases such as “click here” as anchor text is really unhelpful as they give no indication of what information you’re linking to, and will get lost amongst the tons of other “click here” links from all over the site. This also goes double for visitors who use screen readers, as the link will be read aloud to them completely devoid of context.

3. ALT Text
Alt attribute text is the hidden HTML code description of an image that describes what the image is. It’s not visible when viewing images on a web page, but it’s incredibly useful for those with screen readers, or even slow internet, to gain some context about the images being shown on the page. Alt text is extremely helpful for SEO purposes as it directly lets search engines know what the images are referencing. If you include keywords in your alt text, your images are likely to show up in search results, thereby linking directly back to your website.
4. Authority
Authority is the amount of value a search engine assigns to a website or web page in order to decide how well it will rank. Search engines use various factors to determine the level of authority they’re going to give a website, including how old the site is, the quality of its content, the number of backlinks it has, and its loading speed to name a few.
Well established websites or domains will automatically rank higher (even if their newer pages have not gone through the work of climbing the rankings) because they have been given more authority by search engines. This is also why websites with domains like .gov and .edu will automatically rank higher than regular .com or .ca websites. Domain authority is ranked on a scale of 0-100, but only highly popular and established websites, such as Facebook will ever have a score close to 100.
5. Backlink
A backlink (also known as an inbound link) refers to a link in another website’s content that leads back to your site. These are super important for SEO because when search engines see a lot of other sites linking back to your content, they see increased credibility and ascribe more authority to your website. Backlinks can take time to accumulate, but when done the right way, they are extremely beneficial to your search ranking.

6. Bots
Bots are digital programs which scour the internet for information and data collection. They analyze collected information for various purposes, usually for indexing and sharing content. While many bots are very useful, and can process information far faster than any human can, there are also unhelpful bots, such as spam bots which can harm a user’s online experience.
7. Bounce Rate
Bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors to a website who leave without clicking on a secondary page on that same website. A high bounce rate is generally an indicator that users are unsatisfied with some aspect of the experience a website is giving them. Perhaps the content is irrelevant or the site is difficult to navigate – either way, reducing your bounce rate should be a priority, especially if it’s over around 70%, in order to increase the value of your web traffic.
8. CMS
Content management systems are programs that allow people to create websites and other digital assets, typically without needing much coding knowledge. Content management systems, as opposed to website builders, allow for a vast degree of customization and have greater SEO capabilities, making them the ideal platform for websites that are serious about their search engine ranking.
The most popular CMS by a country mile is WordPress, and for good reason. We custom build almost all of our business websites with WordPress, with excellent results.

9. Conversion
A conversion is when a web user completes any desired action on your website. These are typically simple actions such as subscribing to your email list or completing a purchase, and are very beneficial to track to see how users are interacting with your website. High conversion rates indicate that your website is successful in getting your traffic to follow through on desired actions (usually a result of effective calls to action), while low conversion rates show that there is something about your conversion journey that isn’t resonating with your visitors.
10. Crawling
Crawling is the work of bots to sift through URLs and gather data on behalf of the search engines. Crawling allows search engines to organize, add, and update websites and pages within their index to make sure they are presenting the most relevant sites possible to their searchers at all times. Employing SEO best practices makes your website as accessible as possible to crawlers so that search engines can index them thoroughly.
Crawl errors (when search engines are unable to crawl your URLs) are very detrimental to your SEO efforts, so be sure to keep a constant eye out for them. If search engines can’t crawl your website, traffic is never going to be able to search for or find it.
11. Domain
A domain is a website’s address that shows in the URL at the top of your web browser’s bar. They usually begin with www. (referring to World Wide Web), and end with an extension such as .com, .net, or .org, which can give some indication of the type of website being visited. For example, our domain is ideamarketing.ca – the main text mirrors our company name, Idea Marketing, while the extension .ca shows our visitors that we are based in Canada.
Domains need to be bought (or more accurately, rented) from hosting platforms in order to be used by the website in question, and can be sold when a website is done with them. New domain owners need to be mindful of their domain’s history, however, as any penalties or other problems incurred by previous owners will stay with the domain even if the new owner has nothing to do with them.

12. Dwell Time
Dwell time is an important website metric to monitor as it refers to the amount of time between a user clicking on your site from the search engine results page and then eventually exiting back to it. Dwell time can be a really good indicator of content quality and overall site interest, but it’s also a factor that search engines take into account when presenting websites to their searchers. If your site has a low dwell time, search engines will infer that you are not giving your users a high enough quality experience, and so will show it to other web users less often as well.
13. Heading
Heading tags separate a website’s content into clear, readable sections based on a hierarchy. The heading tag with the highest importance is H1, while the lowest is H6. Every page should only include one H1 tag, as that is the main title of the entire page. Your content should then follow the order of the tags as you present your information. For example, if you have an H2 title and then a section underneath it that requires a subheading, you will use an H3 tag for it. Your next main section can then go back to using an H2 tag, but you would never jump from H2 to H4, for instance.
Using the correct heading titles is important not only for your readers, but for SEO purposes too. The most effective headings include your keywords and are used to headline small, readable chunks of text.
14. Index
An index is where search engines store and reference the data collected by bots during the crawling process. Web pages that are added to the index are then able to appear in search queries because the search engine has successfully determined the page’s content and its quality. Websites with a high indexability are easily crawled by bots and added to the search engines’ index faster.
15. Keyword
A keyword is a word or phrase that websites try to ‘target’ for SEO purposes under the assumption that their specific audience will be searching for that term and others like it. Including keywords in the right places in your website, such as in tags, alt text, content, anchor text, etc, can help search engines associate your website with a high level of relevance in relation to those targeted terms. SEO practitioners have to engage in keyword research to select the topics and terms to target on their website by seeing what web users are already searching for, and how heavy the competition is around those words.
Long-tail keywords, which are longer and more specific variations of a main keyword (usually a lesser searched phrase), are helpful to research and target, especially when the main keyword is highly competitive. Targeting long-tail keywords will reveal user results of quality instead of quantity, which is beneficial as the traffic guided to your website through these terms is much more likely to make conversions.
![]()
16. KPI
KPI stands for key performance indicator, and is a specific measurement used to determine how successfully a website is performing according to a predetermined set of goals. Many SEO efforts are often demonstrated through the standards set by certain KPIs. For instance, if a website owner is measuring revenue growth or customer satisfaction, a highly search engine optimized site will typically return better KPI results than one that is not ranking consistently.
17. Meta Description
A meta description describes a web page’s content in a couple of sentences, so that web users can decide if the site is worth visiting. The meta description is displayed directly under the title tag on the search engine results page. Any words searched specifically by the user will show up bolded if they appear in the meta description. While including these keywords in your meta description doesn’t directly impact SEO performance, it can make your website stand out to users and increase your chances of getting clicks and web traffic.
18. Metric
A metric is a measurement of a website’s performance based on actions that its web traffic takes. The measurement of these metrics is usually conducted through analytics tools such as Google Analytics, which give extensive and accurate data about a website’s visitors and the subsequent behaviour they engage in. Important website metrics to monitor, especially for SEO purposes, include bounce rate, conversion rate, dwell time, and number of visitors.

19. No Index
No index tags let search engines know not to index the URL in question. With no index tags, users will not be able to search for the page directly, but can still access it through links on other webpages. This is especially useful for pages that are only relevant after a specific action (for example “order completed!” pages) and pages that are irrelevant to the general public (for example employee only pages). No index tags help to keep unnecessary pages out of the search engine rankings so that users are only given the highest quality search results.
20. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to search engine optimization efforts that occur outside of a website’s direct control. The most common form of off-page SEO is backlinks received from outside websites, but it includes traffic directed from marketing initiatives such as email marketing, social media marketing, media promotions, etc. It is the hardest type of SEO to control, but if you are given authority by outside sources, search engines value that very highly.
21. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO in contrast, refers to search engine optimization techniques that involve a website’s front end. Much of on-page SEO involves what users can actually see when clicking on a website. This includes optimizing the title tags and meta descriptions, writing high quality content, and having quality images with the appropriate alt text. Also included is the quality of the general navigation and URL structuring of the site. On-page SEO includes some of the most important and easiest to optimize ranking factors for search engines, so they should always be prioritized.
22. Organic Search
Organic search refers to websites which appear on a search engine’s results page without having paid to be displayed. Organic search results notably do not include the “ad” label attached to the paid search results which receive the very best slots on the page. Organic search results are displayed purely based on the rankings assigned to them by the search engine algorithms, and are supposed to show users the most relevant websites to their search queries.

23. Outbound Link
Outbound or external links are links included in a website’s content that direct traffic away to a different website altogether. Outbound links from your website count as backlinks to the external website in question, and aid them in their linking strategy, especially if your website has a high level of authority. Outbound links are not highly important when it comes to your own website’s SEO efforts, but they can help you to build relationships with other websites and may also minimally affect your ranking.
24. Rank
A website’s rank is the position they are awarded on a search engine’s organic results page in regard to a certain search query. Ranking is determined by a wide variety of factors taken into account by the search engine’s complex algorithms, and the main goal of SEO is to improve a website’s rank as much as possible. The higher a website ranks, the more valuable it is considered by the search engine.
25. Responsive Design
Responsive web design is the process of designing a website so that the content and structure automatically adjust to the screen size and specifications of the device it is being accessed on. Also known as mobile friendliness, responsive web design is an incredibly important ranking factor for SEO purposes. With the majority of web users now being mobile browsers, search engines will simply not display websites which are not mobile responsive.

26. Search Engine
Search engines are web programs that allow users to look up or search various queries and receive information from a crawled and indexed list of websites in return. Search engines use a series of algorithms to try and accurately match users’ search requests with the most relevant and high quality information they can find. Websites in turn use search engine optimization techniques to try and get the most visibility they can on the search engine’s results pages. The most popular search engine is Google, but others like Bing, DuckDuckGo and Yahoo are also used by searchers to look up information.
27. SERP
The search engine results page is the ranked list of websites a search engine displays after a user makes a search. It is composed of both paid search results, which take the top, most advantageous spots, and organic search results, which fall underneath them. Depending on the nature of a visitor’s search, other information such as headline news, knowledge panels, maps, related questions, etc may be shown.
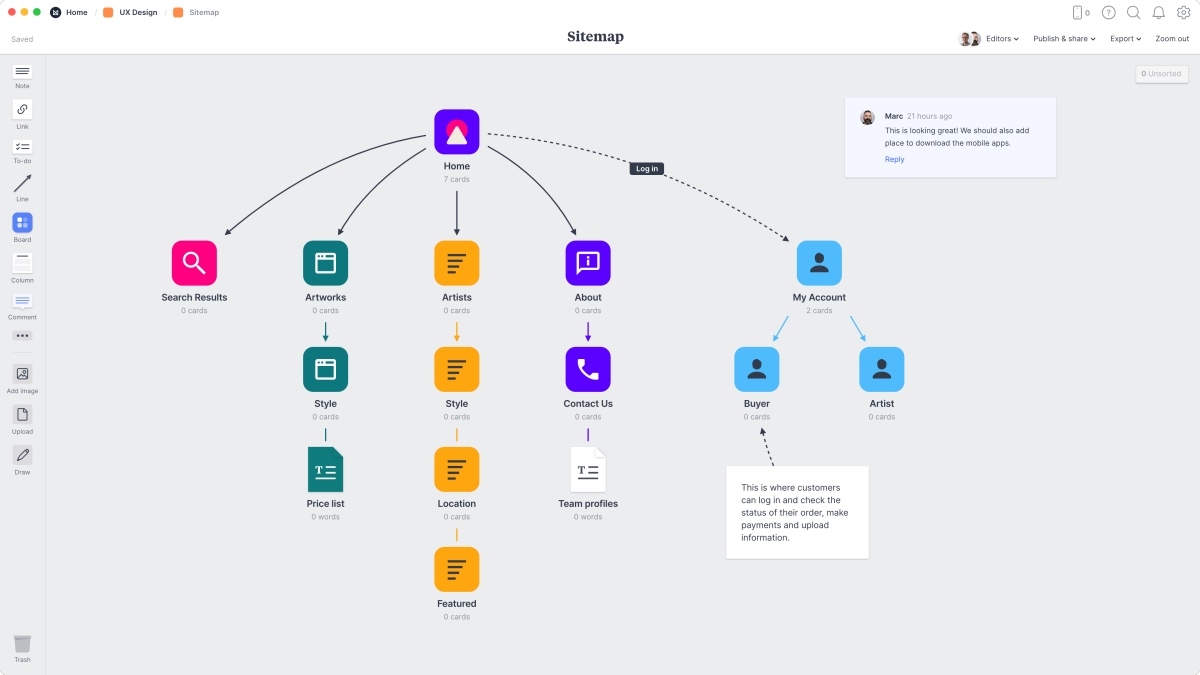
28. Sitemap
A sitemap is a list of pages on a website and their structure and attributes. Sitemaps typically come in two forms. An XML sitemap is for crawlers to understand which pages to index on a website and how they relate to each other. An HTML sitemap helps users to understand the relationship and navigation journey between various web pages. HTML sitemaps are especially essential when conducting new website designs or redesigns.
29. SSL Certificate
A secure sockets layer certificate is a protective addition to a website that encrypts data and conducts identity authentication so that the site and any information that it holds is as secure as possible. SSL certificates change website addresses from http:// to https://, and will show a padlock symbol in the web address bar at the top of the browser. Search engines take security very seriously, so making sure your website is secured with SSL is a top SEO priority.
30. Technical SEO
Technical SEO refers to search engine optimization efforts that involve a website’s back end. Much of technical SEO involves things your users won’t directly see, but will definitely notice the impact of. Steps you can take to improve your website’s technical SEO are to make sure your website’s site structure is robust and intuitive, that your site can be effectively crawled by search engines, that your pages load as fast as possible, and that your web design is responsive. Search engines do not want to display websites that don’t give the best user experience possible, so improving your technical SEO to make sure your site is running as smoothly as possible is a great way to boost your ranking.
31. Title Tag
A title tag is an HTML tag that displays the title of a given website when it’s shown on the search engine results page. Title tags are shown right above the meta description, and tell the user the context of what they are about to click on. Title tags are vital for SEO, and so they should include the keywords you are trying to target, whilst also being readable and eye-catching for viewers. The goal of a title tag is to get users to click on your page in 65 characters or less, while also ranking the site as high as possible.
32. URL
A uniform resource locator is the full version of a web address (https://…, www….) that leads a browser to access a website or web page. It is composed of a string of letters and numbers that give the search engine specific pieces of information about the resource in question. Parameters can be added to URLs to track certain information, such as where web traffic came from to reach the web page they are on.

SEO Going Forward
While this SEO term list is by no means a complete SEO glossary with the most important SEO terms for beginners, it’s a great place to start to fill in some of the gaps on your SEO journey. Having a basic understanding of these SEO terms for beginners, and then implementing the SEO strategies they relate to will get you well on your way to a website that climbs the search engine rankings with ease. If you’re looking for further guidance on optimizing your blog posts for SEO and enhancing your search engine ranking, our article on How to Optimize Your Blog Post for SEO is a valuable resource.Remember that building search results organically takes time, patience, and consistent monitoring, but it is so worth it in the end.
We at Idea Marketing would love to help with your search engine optimization strategy so that your website can attract the traffic it deserves. Contact us today to find out more!